Greetings Miners! What is Layer 2 technology, and how does it help blockchain systems deal with the problems of scalability and transaction speed?
As blockchain technology advances, addressing scalability and transaction efficiency remains a key challenge. An alternative called Layer 2 offers a useful solution to these problems, making transactions both quicker and cheaper while still maintaining the security and decentralization of Layer 1.
This guide provides an overview of Layer 2 in the cryptocurrency industry, detailing what it is, its significance, and its potential impact on blockchain systems.
Let’s Dive Into It!
Table of Contents
Layers of Blockchain Technology
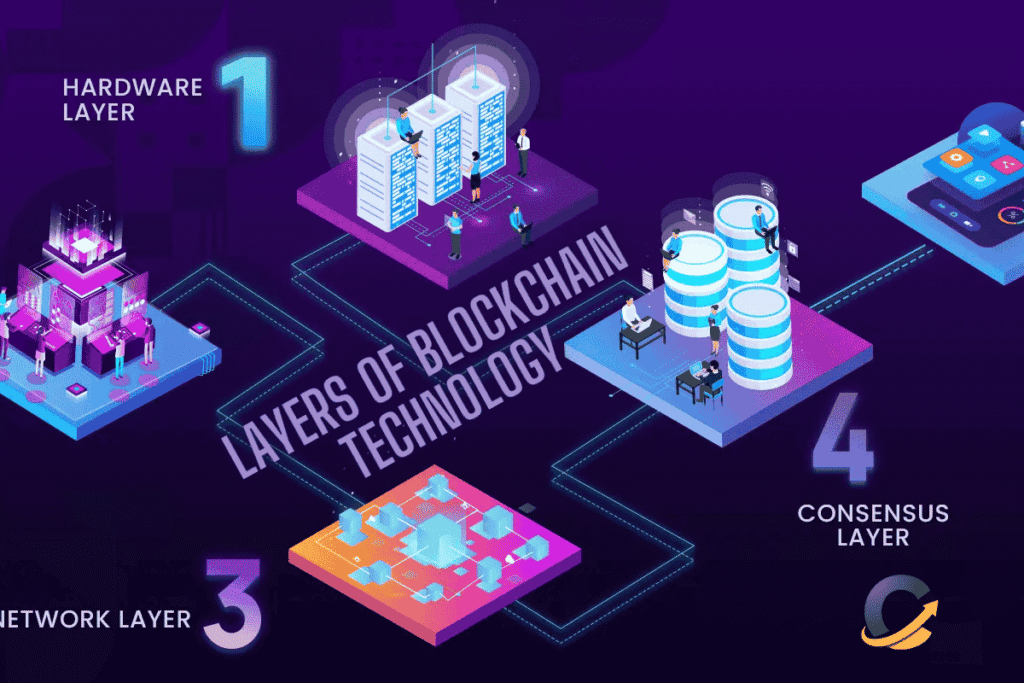
In a blockchain, layers represent independent parts where various protocols collaborate to achieve set functions. The most important layers consist of
- Layer 0 forms the base and holds protocols that enable information sharing and collaboration between different blockchains.
- The first layer, known as the base, holds blockchain networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which ensure consensus, security, and access to data.
BlockSpaces
In Layer 2, secondary frameworks are constructed over existing blockchains to enhance their ability to process numerous transactions.
What Do We Mean by Layer 2
A group of off-chain solutions and protocols, known as Layer 2, rests on top of existing Layer 1 blockchains. The purpose of these solutions is to expedite transaction handling by first processing them off the main chain and then transferring the final status to Layer 1.
Because transaction processing moves to Layer 2, these solutions prevent network congestion, lower transaction costs, and boost the network’s speed, all without compromising the blockchain’s security or decentralization.
Layer 2-like Ethereum Needed to be Addressed
The urgent need for Layer 2 solutions comes from the core shortcomings of Layer 1 blockchains.
- Many existing layer 1 blockchains cannot handle a high volume of transactions, which means they are slower to act.
- The congestion of the blockchain can drive up transaction fees, making it tough to do small online transactions.
- Users may not be interested in blockchain if it takes too long to process transactions and incurs excessive costs.
Solutions from Layer 2
Enable the handling of numerous transactions with minimal delay and at lower costs, thereby creating a pleasant experience for users and motivating more people to participate.
Solutions that Support Layer 2 Connection
Several Layer 2 solutions have been developed, each with its own mechanism and use case.
State Channels
Two parties can trade several times without ever recording those transactions on the blockchain.
With this approach, on-chain transactions are significantly reduced, allowing for quicker and more cost-effective usage.
Micropayments, gaming, and delivering services in real-time can all utilize blockchain technology.
Sidechains
Sidechains operate in conjunction with the main chain, utilizing a two-way connection. Each blockchain can use its method to agree on transactions and handle them individually, checking against the main chain at regular intervals.
Use Cases
Adaptable applications that utilize various rules for approval or standards for their tokens.
Rollups
- Smart contracts perform rollups outside of the main blockchain and verify the outcomes inside the main chain.
- With optimistic rollups, transactions are approved automatically until any misconduct is detected.
- Transactions on zero-knowledge rollups are validated using proofs, rather than sharing details of actual transactions.
Applications
DeFi, NFTs, and basic dApps.
Plasma
Plasma chains are secondary chains that manage transaction processing and, on occasion, synchronize their status updates with the parent blockchain. They use fraud-proof measures to maintain their safety.
For high-throughput applications such as gaming and microtransactions, use cases.
Popular Way to Extend Blockchain Scaling
Several Layer 2 networks are renowned for their ability to enhance scalability.
Arbitrum
Arbitrum is a way to enhance Ethereum using Optimistic Rollup, which enables greater throughput and lower costs.
Optimism
A simple and compatible optimistic rollup platform like the other systems on Ethereum.
ZkSync provides users with the opportunity for fast, safe, and economical transactions through its ZK Rollup service.
Polygon
Polygon (formerly known as Matic) offers solutions such as Plasma chains and rollups to enhance the speed and throughput of Ethereum.
StarkNet: Wild animation
What Layer 2 Solutions Have to Offer
There are many benefits to using Layer 2 solutions.
Handling transactions off-chain enables Layer 2 to process transactions much faster (thousands per second).
Because there are fewer transactions on-chain, it’s possible to send and receive very small amounts with low costs.
Rapid Innovation
Better Use by Users: Improved confirmations and cheaper usage make life easier for people who use cryptocurrencies.
Large User Numbers
Applications can serve a wide range of users without compromising their performance.
Certain Layer 2 solutions help different blockchains interact with each other, opening up new areas for the ecosystem.
The Things to Keep in Mind and Address
At the same time, Layer 2 efforts come with some potential challenges.
- If not secured well, the transactions made on external networks can create security problems.
- Adding Layer 2 solutions can complicate the development and interaction of applications.
- Scenes where Layer 2s strike a balance between decentralization and scalability can occur.
- Liquidity can become split if assets are maintained on a collection of Layer 2 solutions.
- The transition to Layer 2 systems should be clearly explained to users and supported by a seamless onboarding process.
What is to Come for Layer 2
Blockchain adoption could be widespread when Layer 2 solutions continue to improve. Possible coming changes include:
Enhancing how blockchain technology communicates to integrate disparate blockchain networks.
Forming common guidelines for Layer 2 solutions that create smooth integration and wider adoption.
Decentralized Sequencers
This approach reduces the risk of a single failure by distributing the sequencing of transactions.
Integration with Sharding from Layer 1
Bringing together Layer 1 sharding to support better scaling on Ethereum.
Creating interfaces that anyone can use and find straightforward when dealing with Layer 2 technologies.
Conclusion
They have helped address many of the issues surrounding the effective and efficient use of blockchain. Because they facilitate faster and less expensive payments, they open doors for more people to use decentralized apps and services. As Layer 2 develops, new ideas and joint efforts are necessary to address current problems and unlock its greatest benefits in the crypto world.
What new ideas and partnerships are needed to make the most of Layer 2 solutions in the cryptocurrency ecosystem?
Frequently Asked Questions, also known as FAQs
- How are Layer 1 and Layer 2 different in the world of cryptocurrency?
Layer 1 refers to the first level of software, which handles and records all transactions directly through the blockchain and without the involvement of third parties. Layer 2 involves applying additional solutions on top of Layer 1 to manage most transactions outside of the main chain and then communicating the results back to it. By using Layer 2, it becomes possible to manage traffic and save money on Layer 1.
- Is it secure to implement solutions on Layer 2?
Generally, Layer 2 projects are secure since they build on the security system of their original Layer 1 blockchain. Even so, each Layer 2 approach has its unique design. A Layer 2’s security is determined by its approach to handling fraud proofs, making data accessible, remaining decentralized, and managing smart contract risks. Audited and commonly used Layer 2 networks, such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync, are smart choices.
- Do I have to move Ethereum onto a Layer 2 to access it?
Yes. Generally, you need to bridge your ETH or tokens from Layer 1 of Ethereum to the Layer 2 chain for interaction. With this approach, you first use a channel or connection from the Layer 2 network, allowing you to spend your money faster and more cost-effectively than on Layer 1.
- If you’re just starting, which Layer 2 solution should you use?
Consider Polygon (through its Proof-of-Stake chain) or Arbitrum One if you are new to blockchain. Most wallets and dApps are set up for these networks, and fees here are hardly ever more than a cent. A growing number of major DeFi platforms are now backing Optimism and zkSync due to their user-friendliness.
- Will implementing sharding on Ethereum still make Layer 2 solutions helpful?
Yes. Even after sharding, Layer 2 options will still play a key role in Ethereum’s development. In reality, sharding and Layer 2s have been created to support each other. Sharding will ensure that data is available, while Layer 2s handle transactions, allowing Ethereum to support many users without compromising its central and secure nature.

